Article contents
The development of magnetic field line wander in gyrokinetic plasma turbulence: dependence on amplitude of turbulence
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 May 2017
Abstract
The dynamics of a turbulent plasma not only manifests the transport of energy from large to small scales, but also can lead to a tangling of the magnetic field that threads through the plasma. The resulting magnetic field line wander can have a large impact on a number of other important processes, such as the propagation of energetic particles through the turbulent plasma. Here we explore the saturation of the turbulent cascade, the development of stochasticity due to turbulent tangling of the magnetic field lines and the separation of field lines through the turbulent dynamics using nonlinear gyrokinetic simulations of weakly collisional plasma turbulence, relevant to many turbulent space and astrophysical plasma environments. We determine the characteristic time 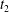 $t_{2}$ for the saturation of the turbulent perpendicular magnetic energy spectrum. We find that the turbulent magnetic field becomes completely stochastic at time
$t_{2}$ for the saturation of the turbulent perpendicular magnetic energy spectrum. We find that the turbulent magnetic field becomes completely stochastic at time 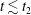 $t\lesssim t_{2}$ for strong turbulence, and at
$t\lesssim t_{2}$ for strong turbulence, and at 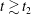 $t\gtrsim t_{2}$ for weak turbulence. However, when the nonlinearity parameter of the turbulence, a dimensionless measure of the amplitude of the turbulence, reaches a threshold value (within the regime of weak turbulence) the magnetic field stochasticity does not fully develop, at least within the evolution time interval
$t\gtrsim t_{2}$ for weak turbulence. However, when the nonlinearity parameter of the turbulence, a dimensionless measure of the amplitude of the turbulence, reaches a threshold value (within the regime of weak turbulence) the magnetic field stochasticity does not fully develop, at least within the evolution time interval 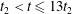 $t_{2}<t\leqslant 13t_{2}$. Finally, we quantify the mean square displacement of magnetic field lines in the turbulent magnetic field with a functional form
$t_{2}<t\leqslant 13t_{2}$. Finally, we quantify the mean square displacement of magnetic field lines in the turbulent magnetic field with a functional form 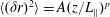 $\langle (\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}r)^{2}\rangle =A(z/L_{\Vert })^{p}$ (
$\langle (\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}r)^{2}\rangle =A(z/L_{\Vert })^{p}$ (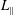 $L_{\Vert }$ is the correlation length parallel to the magnetic background field
$L_{\Vert }$ is the correlation length parallel to the magnetic background field 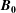 $\boldsymbol{B}_{\mathbf{0}}$,
$\boldsymbol{B}_{\mathbf{0}}$,  $z$ is the distance along
$z$ is the distance along 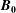 $\boldsymbol{B}_{\mathbf{0}}$ direction), providing functional forms of the amplitude coefficient
$\boldsymbol{B}_{\mathbf{0}}$ direction), providing functional forms of the amplitude coefficient 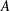 $A$ and power-law exponent
$A$ and power-law exponent 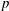 $p$ as a function of the nonlinearity parameter.
$p$ as a function of the nonlinearity parameter.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2017
References
- 6
- Cited by


