Article contents
Novel 4ZnO⋅B2O3⋅H2O:Ln3+/HTC (where Ln = Eu or Tb) phosphors: Synthesis, morphology and luminescence properties
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 June 2020
Abstract
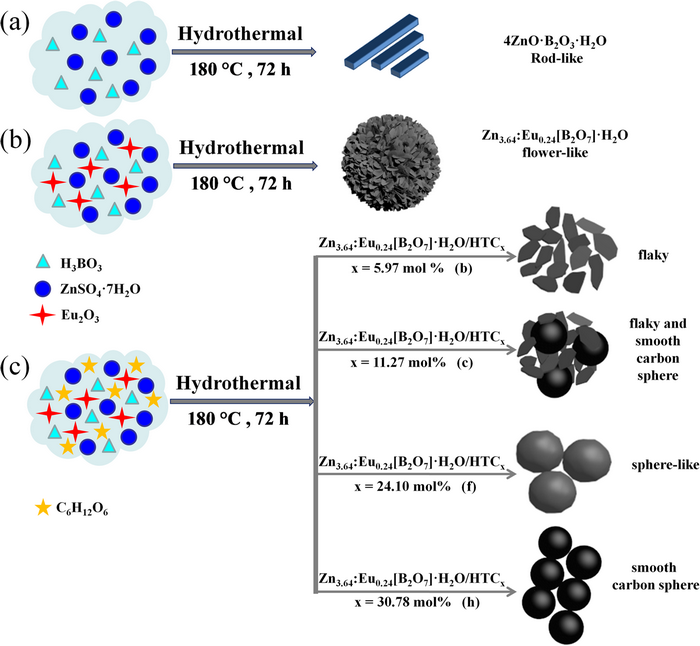
Hydrothermal carbon microsphere (HTC) is a carbon-based fluorescent material, which can be synthesized by hydrothermal carbonization of glucose. In this article, a series of 4ZnO·B2O3·H2O:Ln3+/HTC (where Ln = Eu or Tb) composites were prepared under hydrothermal conditions. The effects of the glucose concentration on the morphology, photoluminescence (PL) intensity and emission color of Zn3.64:Eu0.24[B2O7]·H2O/HTCx and Zn3.55:Tb0.3[B2O7]·H2O/HTCy were investigated. The relationship between morphology and PL intensity of composites was discussed. The results revealed that the presence of HTC did not change the original emission color of 4ZnO·B2O3·H2O:Ln3+ (where Ln = Eu or Tb) materials, but greatly increased their PL intensity, the sphere-like morphology composites have the strongest PL intensity. The Zn3.64:Eu0.24[B2O7]·H2O/HTCx and Zn3.55:Tb0.3[B2O7]·H2O/HTCy emit bright red light and green light, respectively, under respective excitation wavelengths. The present research suggests that the 4ZnO·B2O3·H2O:Ln3+/HTC (where Ln = Eu or Tb) composites may be candidates of red and green phosphors for display and lighting applications.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 35 , Issue 13: Focus Section: Interactions of Shear Transformation Bands , 14 July 2020 , pp. 1680 - 1691
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2020
References
- 4
- Cited by





