Article contents
Nanoindentation creep in polycarbonate and syndiotactic polystyrene
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 February 2012
Abstract
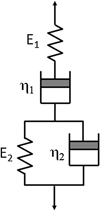
This study focuses on nanoindentation creep in polycarbonate (PC) and syndiotactic polystyrene (sPS) throughout the transient and steady-state regions. The viscoelastic Burgers model is used to explain transient creep data, while the power-law creep model is used to interpret steady-state creep data. The Newtonian shear viscosity of the Maxwell element and Young’s modulus of the Kelvin element are greater for the creep period than for the preload period, and an opposite trend is noted in the Newtonian shear viscosity of the Kelvin element and Young’s modulus of the Maxwell element. The fact that the Young’s moduli of Maxwell and Kelvin elements in the creep period are different from those in the preload period implies that a stress-induced mesomorphic structure forms or that crystallization occurs in nanoindentation creep. While the strain rate increases with decreasing preload period, the stress exponent factor is almost the same for all preload periods.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by


