Article contents
Fabrication and magnetic properties of ordered Co100−xPbx nanowire arrays electrodeposited in AAO templates: Effects of annealing temperature and frequency
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 March 2017
Abstract
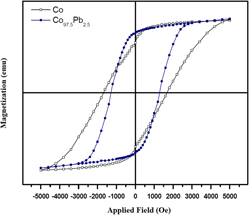
CoxPb1−x nanowire arrays within an anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) template were electrodeposited from an appropriate acetate bath by applying alternating current (ac). The effect of the Pb content on magnetic properties of nanowire arrays was investigated. By adding Pb2+ to an electrolyte containing Co2+, the coercivity field of nanowires decreased from 1508 Oe in Co100 to 921 Oe in Co92.5Pb7.5 while squareness increased from 0.74 for Co nanowires to about 0.82 for Co92.5Pb7.5 nanowire alloy sample. The effect of annealing on the magnetic properties of nanowires in the temperature range between 300 °C and 600 °C was also investigated. It was observed that the coercivity field of Co97.5Pb2.5 nanowire increases from 1290 Oe at room temperature to 1785 Oe at 600 °C. Furthermore, the effect of electrodeposition frequency on the magnetic properties of Co97.5Pb2.5 nanowires was studied. The coercivity was enhanced with increasing frequency; however, after annealing all samples exhibited enhanced coercivity regardless of the electrodeposition frequency.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Amit Goyal
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by



