Article contents
Synthesis, crystal structure, photoluminescence, and electroluminescence properties of a new compound containing diphenylmethylene, carbazole, and malononitrile units
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 June 2019
Abstract
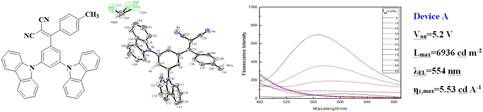
In this work, a new phenylethylene derivative, named 2-((3,5-di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)(p-tolyl)methylene)malononitrile (DCPTMM), is synthesized and characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR spectroscopies, mass spectrum, and X-ray crystallography. Its photophysical properties are systematically studied and the result illustrates that DCPTMM shows aggregation-induced emission (AIE). The X-ray single crystal diffraction shows that the individual structure of crystals is monoclinic system with space group symbol P21/c and presents a twisted propeller-type structure as well as the packing structure of crystals has multiple types of hydrogen bonds (C–H⋯π and C–H⋯N) formed between adjacent molecules, and there is no π–π interaction between the aromatic rings, which is the main reason for the formation of AIE. Nondoped OLED fabricated with DCPTMM as light emitting layer emits greenish yellow light with a maximum emission peak of 554 nm and has relatively good performance with a maximum current efficiency of 5.53 cd/A and a maximum brightness of 6936 cd/m2.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 34 , Issue 17: Focus Issue: Building Advanced Materials via Particle Aggregation and Molecular Self-Assembly , 16 September 2019 , pp. 3000 - 3010
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
References
- 1
- Cited by


