Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tchoufag, J.
Magnaudet, J.
and
Fabre, D.
2013.
Linear stability and sensitivity of the flow past a fixed oblate spheroidal bubble.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 5,
Auguste, Franck
Magnaudet, Jacques
and
Fabre, David
2013.
Falling styles of disks.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 719,
Issue. ,
p.
388.
Tchoufag, Joël
Fabre, David
and
Magnaudet, Jacques
2014.
Global linear stability analysis of the wake and path of buoyancy-driven disks and thin cylinders.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 740,
Issue. ,
p.
278.
Uhlmann, Markus
and
Dušek, Jan
2014.
The motion of a single heavy sphere in ambient fluid: A benchmark for interface-resolved particulate flow simulations with significant relative velocities.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 59,
Issue. ,
p.
221.
Chrust, M.
Bouchet, G.
and
Dušek, J.
2014.
Effect of solid body degrees of freedom on the path instabilities of freely falling or rising flat cylinders.
Journal of Fluids and Structures,
Vol. 47,
Issue. ,
p.
55.
Izard, Edouard
Bonometti, Thomas
and
Lacaze, Laurent
2014.
Modelling the dynamics of a sphere approaching and bouncing on a wall in a viscous fluid.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 747,
Issue. ,
p.
422.
Tchoufag, Joël
Magnaudet, Jacques
and
Fabre, David
2014.
Linear instability of the path of a freely rising spheroidal bubble.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 751,
Issue. ,
Tchoufag, Joël
Fabre, David
and
Magnaudet, Jacques
2015.
Weakly Nonlinear Model with Exact Coefficients for the Fluttering and Spiraling Motion of Buoyancy-Driven Bodies.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 115,
Issue. 11,
Zhou, W.
and
Dušek, J.
2015.
Chaotic states and order in the chaos of the paths of freely falling and ascending spheres.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 75,
Issue. ,
p.
205.
Yu, Haitao
Lu, Ziyang
Lohse, Detlef
and
Zhang, Xuehua
2015.
Gravitational Effect on the Formation of Surface Nanodroplets.
Langmuir,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 46,
p.
12628.
Cano-Lozano, José Carlos
Martínez-Bazán, Carlos
Magnaudet, Jacques
and
Tchoufag, Joël
2016.
Paths and wakes of deformable nearly spheroidal rising bubbles close to the transition to path instability.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 5,
Citro, V.
Tchoufag, J.
Fabre, D.
Giannetti, F.
and
Luchini, P.
2016.
Linear stability and weakly nonlinear analysis of the flow past rotating spheres.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 807,
Issue. ,
p.
62.
Akiki, G.
Moore, W.C.
and
Balachandar, S.
2017.
Pairwise-interaction extended point-particle model for particle-laden flows.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 351,
Issue. ,
p.
329.
Loisy, Aurore
Naso, Aurore
and
Spelt, Peter D. M.
2017.
Buoyancy-driven bubbly flows: ordered and free rise at small and intermediate volume fraction.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 816,
Issue. ,
p.
94.
Lācis, Uǧis
Olivieri, Stefano
Mazzino, Andrea
and
Bagheri, Shervin
2017.
Passive control of a falling sphere by elliptic-shaped appendages.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 3,
Dušek, J.
2017.
Particles in Flows.
p.
397.
Fabre, David
Tchoufag, Joël
Citro, Vincenzo
Giannetti, Flavio
and
Luchini, Paolo
2017.
The flow past a freely rotating sphere.
Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 5-6,
p.
475.
Zhou, W.
Chrust, M.
and
Dušek, J.
2017.
Path instabilities of oblate spheroids.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 833,
Issue. ,
p.
445.
Pierson, Jean-Lou
and
Magnaudet, Jacques
2018.
Inertial settling of a sphere through an interface. Part 2. Sphere and tail dynamics.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 835,
Issue. ,
p.
808.
Auguste, Franck
and
Magnaudet, Jacques
2018.
Path oscillations and enhanced drag of light rising spheres.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 841,
Issue. ,
p.
228.
 (defined as that between the disk axis and its velocity) is small. We derive the structure of the steady flow past the body and the associated hydrodynamic force and torque through a weakly nonlinear expansion of the flow with respect to
(defined as that between the disk axis and its velocity) is small. We derive the structure of the steady flow past the body and the associated hydrodynamic force and torque through a weakly nonlinear expansion of the flow with respect to  . When buoyancy drives the body motion, we obtain a solution corresponding to an oblique path with a non-zero incidence by requiring the torque to vanish and the hydrodynamic and net buoyancy forces to balance each other. This oblique solution is shown to arise through a bifurcation at a critical Reynolds number
. When buoyancy drives the body motion, we obtain a solution corresponding to an oblique path with a non-zero incidence by requiring the torque to vanish and the hydrodynamic and net buoyancy forces to balance each other. This oblique solution is shown to arise through a bifurcation at a critical Reynolds number  which does not depend upon the body-to-fluid density ratio and is distinct from the critical Reynolds number
which does not depend upon the body-to-fluid density ratio and is distinct from the critical Reynolds number 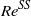 corresponding to the steady bifurcation of the flow past the body held fixed with
corresponding to the steady bifurcation of the flow past the body held fixed with 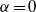 . We then apply the same approach to the related problem of a sphere that weakly rotates about an axis perpendicular to its path and show that an oblique path sets in at a critical Reynolds number
. We then apply the same approach to the related problem of a sphere that weakly rotates about an axis perpendicular to its path and show that an oblique path sets in at a critical Reynolds number 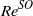 slightly lower than
slightly lower than 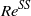 , in agreement with available numerical studies.
, in agreement with available numerical studies.

