Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Bandaru, Vinodh
Kolchinskaya, Anastasiya
Padberg-Gehle, Kathrin
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2015.
Role of critical points of the skin friction field in formation of plumes in thermal convection.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 4,
Ostilla-Monico, R.
Yang, Yantao
van der Poel, E.P.
Lohse, D.
and
Verzicco, R.
2015.
A multiple-resolution strategy for Direct Numerical Simulation of scalar turbulence.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 301,
Issue. ,
p.
308.
Zhou, Sheng-Qi
Xie, Yi-Chao
Sun, Chao
and
Xia, Ke-Qing
2016.
Statistical characterization of thermal plumes in turbulent thermal convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 5,
De Paoli, Marco
Zonta, Francesco
and
Soldati, Alfredo
2016.
Influence of anisotropic permeability on convection in porous media: Implications for geological CO2 sequestration.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 5,
Guha, Abhijit
and
Sengupta, Sayantan
2016.
Effects of finiteness on the thermo-fluid-dynamics of natural convection above horizontal plates.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 6,
Zhang, Yang
Zhou, Quan
and
Sun, Chao
2017.
Statistics of kinetic and thermal energy dissipation rates in two-dimensional turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 814,
Issue. ,
p.
165.
Dabbagh, F.
Trias, F. X.
Gorobets, A.
and
Oliva, A.
2017.
A priori study of subgrid-scale features in turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 10,
Guo, Shuang-Xi
Zhou, Sheng-Qi
Qu, Ling
Cen, Xian-Rong
and
Lu, Yuan-Zheng
2017.
Evolution and statistics of thermal plumes in tilted turbulent convection.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 111,
Issue. ,
p.
933.
Jiang, Hechuan
Zhu, Xiaojue
Mathai, Varghese
Verzicco, Roberto
Lohse, Detlef
and
Sun, Chao
2018.
Controlling Heat Transport and Flow Structures in Thermal Turbulence Using Ratchet Surfaces.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 120,
Issue. 4,
Huang, Xiao-Jie
Li, You-Rong
Zhang, Li
and
Hu, Yu-Peng
2018.
Turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection in a cubical container filled with cold water near its maximum density.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 127,
Issue. ,
p.
21.
Jiang, Linfeng
Sun, Chao
and
Calzavarini, Enrico
2019.
Robustness of heat transfer in confined inclined convection at high Prandtl number.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 99,
Issue. 1,
Zou, Hong-Yue
Zhou, Wen-Feng
Chen, Xi
Bao, Yun
Chen, Jun
and
She, Zhen-Su
2019.
Boundary layer structure in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a slim box.
Acta Mechanica Sinica,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 4,
p.
713.
Soucasse, Laurent
Podvin, Bérengère
Rivière, Philippe
and
Soufiani, Anouar
2020.
Reduced-order modelling of radiative transfer effects on Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a cubic cell.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 898,
Issue. ,
Dabbagh, F.
Trias, F. X.
Gorobets, A.
and
Oliva, A.
2020.
Flow topology dynamics in a three-dimensional phase space for turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 2,
Zhao, Wenxuan
Ye, Wei
Xue, Yu
Wu, Chao
and
Zhang, Xu
2020.
Ventilation schemes for high-temperature buoyancy-driven plumes from spherical surfaces of a large-scale experimental facility.
Energy and Built Environment,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 3,
p.
262.
Qiao, Manman
Tian, Zhao Feng
Yang, Qingshan
and
Xu, Feng
2020.
Transition to chaos for buoyant flows in a groove heated from below.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 5,
Wang, Bo-Fu
Zhou, Quan
and
Sun, Chao
2020.
Vibration-induced boundary-layer destabilization achieves massive heat-transport enhancement.
Science Advances,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 21,
Trias, F. X.
Dabbagh, F.
Gorobets, A.
and
Oliet, C.
2020.
On a Proper Tensor-Diffusivity Model for Large-Eddy Simulation of Buoyancy-Driven Turbulence.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 105,
Issue. 2,
p.
393.
Li, Xiao-Ming
Huang, Shi-Di
Ni, Rui
and
Xia, Ke-Qing
2021.
Lagrangian velocity and acceleration measurements in plume-rich regions of turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 5,
Zhou, Wen-Feng
and
Chen, Jun
2021.
Large-scale structures of turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a slim-box.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 6,
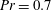 $\mathit{Pr}=0.7$ fluid up to
$\mathit{Pr}=0.7$ fluid up to  $\mathit{Ra}=10^{12}$ are used to study the statistics of thermal plumes. At various vertical locations in a cylindrical set-up with aspect ratio
$\mathit{Ra}=10^{12}$ are used to study the statistics of thermal plumes. At various vertical locations in a cylindrical set-up with aspect ratio 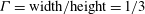 ${\it\Gamma}=\text{width}/\text{height}=1/3$, plumes are identified and their properties extracted. It is found that plumes are much less likely to be emitted from plate regions with large wind shear. Close to the plates, the plumes have a unimodal log–normal distribution, whereas at more central locations the distribution becomes weakly bimodal, which can be traced back to clustering of the plumes and influence of the large-scale circulation. The number of hot plumes decreases with height. The width of the plumes scales with
${\it\Gamma}=\text{width}/\text{height}=1/3$, plumes are identified and their properties extracted. It is found that plumes are much less likely to be emitted from plate regions with large wind shear. Close to the plates, the plumes have a unimodal log–normal distribution, whereas at more central locations the distribution becomes weakly bimodal, which can be traced back to clustering of the plumes and influence of the large-scale circulation. The number of hot plumes decreases with height. The width of the plumes scales with 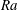 $\mathit{Ra}$ approximately as
$\mathit{Ra}$ approximately as 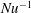 $\mathit{Nu}^{-1}$, indicating that it is determined by the thermal boundary layer thickness.
$\mathit{Nu}^{-1}$, indicating that it is determined by the thermal boundary layer thickness.




