Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Sondak, David
Smith, Leslie M.
and
Waleffe, Fabian
2015.
Optimal heat transport solutions for Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 784,
Issue. ,
p.
565.
Bandaru, Vinodh
Kolchinskaya, Anastasiya
Padberg-Gehle, Kathrin
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2015.
Role of critical points of the skin friction field in formation of plumes in thermal convection.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 4,
Sakievich, P.J.
Peet, Y.T.
and
Adrian, R.J.
2016.
Large-scale thermal motions of turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a wide aspect-ratio cylindrical domain.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 61,
Issue. ,
p.
183.
Schumacher, Jörg
Bandaru, Vinodh
Pandey, Ambrish
and
Scheel, Janet D.
2016.
Transitional boundary layers in low-Prandtl-number convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 8,
Pratt, J.
Baraffe, I.
Goffrey, T.
Geroux, C.
Viallet, M.
Folini, D.
Constantino, T.
Popov, M.
and
Walder, R.
2016.
Spherical-shell boundaries for two-dimensional compressible convection in a star.
Astronomy & Astrophysics,
Vol. 593,
Issue. ,
p.
A121.
Abram, Christopher
Pougin, Miriam
and
Beyrau, Frank
2016.
Temperature field measurements in liquids using ZnO thermographic phosphor tracer particles.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 7,
Pandey, Ambrish
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2017.
Turbulent superstructures in Rayleigh‐Bénard convection for varying Prandtl numbers.
PAMM,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 1,
p.
15.
Giannakis, Dimitrios
Kolchinskaya, Anastasiya
Krasnov, Dmitry
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2018.
Koopman analysis of the long-term evolution in a turbulent convection cell.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 847,
Issue. ,
p.
735.
Schneide, Christiane
Pandey, Ambrish
Padberg-Gehle, Kathrin
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2018.
Probing turbulent superstructures in Rayleigh-Bénard convection by Lagrangian trajectory clusters.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 11,
Shcheritsa, Olga Vladimirovna
and
Mazhorova, Olga Semenovna
2018.
Methods for study the flow of complex structure.
Keldysh Institute Preprints,
p.
1.
De, A.K.
Eswaran, V.
and
Mishra, P.K.
2018.
Dynamics of plumes in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids,
Vol. 72,
Issue. ,
p.
164.
Aurnou, Jonathan M.
Bertin, Vincent
Grannan, Alexander M.
Horn, Susanne
and
Vogt, Tobias
2018.
Rotating thermal convection in liquid gallium: multi-modal flow, absent steady columns.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 846,
Issue. ,
p.
846.
Stevens, Richard J. A. M.
Blass, Alexander
Zhu, Xiaojue
Verzicco, Roberto
and
Lohse, Detlef
2018.
Turbulent thermal superstructures in Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 4,
Pandey, Ambrish
Scheel, Janet D.
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2018.
Turbulent superstructures in Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 1,
Cook, Robert
2019.
Observations of patterned flow in slush on a small pond.
Limnologica,
Vol. 78,
Issue. ,
p.
125713.
Fonda, Enrico
Pandey, Ambrish
Schumacher, Jörg
and
Sreenivasan, Katepalli R.
2019.
Deep learning in turbulent convection networks.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 116,
Issue. 18,
p.
8667.
König, Jörg
Moller, Sebastian
Granzow, Nicolai
and
Cierpka, Christian
2019.
On the application of a supercontinuum white light laser for simultaneous measurements of temperature and velocity fields using thermochromic liquid crystals.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
Vol. 109,
Issue. ,
p.
109914.
Cierpka, Christian
Kästner, Christian
Resagk, Christian
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2019.
On the challenges for reliable measurements of convection in large aspect ratio Rayleigh-Bénard cells in air and sulfur-hexafluoride.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
Vol. 109,
Issue. ,
p.
109841.
Ibbeken, Gregor
Green, Gerrit
and
Wilczek, Michael
2019.
Large-Scale Pattern Formation in the Presence of Small-Scale Random Advection.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 123,
Issue. 11,
Schneide, Christiane
Stahn, Martin
Pandey, Ambrish
Junge, Oliver
Koltai, Péter
Padberg-Gehle, Kathrin
and
Schumacher, Jörg
2019.
Lagrangian coherent sets in turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 5,
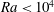 $\mathit{Ra}<10^{4}$, continue to exist in three-dimensional numerical simulations of turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in extended cylindrical cells with an aspect ratio
$\mathit{Ra}<10^{4}$, continue to exist in three-dimensional numerical simulations of turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in extended cylindrical cells with an aspect ratio 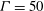 ${\it\Gamma}=50$ and
${\it\Gamma}=50$ and 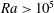 $\mathit{Ra}>10^{5}$. They are revealed when the turbulent fields are averaged in time and turbulent fluctuations are thus removed. We apply the Boussinesq closure to estimate turbulent viscosities and diffusivities, respectively. The resulting turbulent Rayleigh number
$\mathit{Ra}>10^{5}$. They are revealed when the turbulent fields are averaged in time and turbulent fluctuations are thus removed. We apply the Boussinesq closure to estimate turbulent viscosities and diffusivities, respectively. The resulting turbulent Rayleigh number 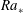 $\mathit{Ra}_{\ast }$, that describes the convection of the mean patterns, is indeed in the SDC range. The turbulent Prandtl numbers are smaller than one, with
$\mathit{Ra}_{\ast }$, that describes the convection of the mean patterns, is indeed in the SDC range. The turbulent Prandtl numbers are smaller than one, with 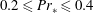 $0.2\leqslant \mathit{Pr}_{\ast }\leqslant 0.4$ for Prandtl numbers
$0.2\leqslant \mathit{Pr}_{\ast }\leqslant 0.4$ for Prandtl numbers 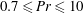 $0.7\leqslant \mathit{Pr}\leqslant 10$. Finally, we demonstrate that these mean flow patterns are robust to an additional finite-amplitude sidewall forcing when the level of turbulent fluctuations in the flow is sufficiently high.
$0.7\leqslant \mathit{Pr}\leqslant 10$. Finally, we demonstrate that these mean flow patterns are robust to an additional finite-amplitude sidewall forcing when the level of turbulent fluctuations in the flow is sufficiently high.


