Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Guerrero, Byron
Lambert, Martin F.
and
Chin, Rey C.
2020.
Extreme wall shear stress events in turbulent pipe flows: spatial characteristics of coherent motions.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 904,
Issue. ,
Baidya, R.
Scharnowski, S.
Bross, M.
and
Kähler, C. J.
2020.
Interactions between a shock and turbulent features in a Mach 2 compressible boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 893,
Issue. ,
Scharnowski, Sven
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2020.
Particle image velocimetry - Classical operating rules from today’s perspective.
Optics and Lasers in Engineering,
Vol. 135,
Issue. ,
p.
106185.
Reuther, Nico
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2020.
Effect of the intermittency dynamics on single and multipoint statistics of turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 897,
Issue. ,
von Hoesslin, Stefan
Gruendmayer, Juergen
Zeisberger, Andreas
Sommer, Martin S.
Klimesch, Jonathan
Behre, Stephan
Brandies, Henri
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2020.
Visualization of laminar–turbulent transition on rotating turbine blades.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 6,
Eich, Felix
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2020.
Large-scale coherent motions in turbulent boundary layers under an adverse pressure gradient up to flow separation.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 85,
Issue. ,
p.
108645.
Örlü, Ramis
and
Vinuesa, Ricardo
2020.
Instantaneous wall-shear-stress measurements: advances and application to near-wall extreme events.
Measurement Science and Technology,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 11,
p.
112001.
Chin, R. C.
Vinuesa, R.
Örlü, R.
Cardesa, J. I.
Noorani, A.
Chong, M. S.
and
Schlatter, P.
2020.
Backflow events under the effect of secondary flow of Prandtl's first kind.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 7,
Tang, Zhanqi
Fan, Ziye
Chen, Letian
and
Jiang, Nan
2021.
Outer-layer structure arrangements based on the large-scale zero-crossings at moderate Reynolds number.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 8,
Abedinejad, Mohammad Sadegh
Bazdidi-Tehrani, Farzad
and
Mirzaei, Sajad
2021.
Investigation of turbulent flow structures in a wall jet can combustor: application of large eddy simulation.
The European Physical Journal Plus,
Vol. 136,
Issue. 6,
Chen, Qigang
Duan, Yanchong
Zhong, Qiang
Wang, Zhongxiang
and
Huang, Lei
2021.
On the method of determining instantaneous wall shear stress from near-wall velocity measurements in wall turbulence.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 12,
Laskari, Angeliki
and
McKeon, Beverley J.
2021.
Temporal characteristics of the probability density function of velocity in wall-bounded turbulent flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 913,
Issue. ,
Kumar, S. Santosh
Huang, Xinyi
Yang, Xiang
and
Hong, Jiarong
2021.
Three dimensional flow motions in the viscous sublayer.
Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Letters,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 2,
p.
100239.
Shehzad, Muhammad
Sun, Bihai
Jovic, Daniel
Ostovan, Yasar
Cuvier, Christophe
Foucaut, Jean-Marc
Willert, Christian
Atkinson, Callum
and
Soria, Julio
2021.
Investigation of large scale motions in zero and adverse pressure gradient turbulent boundary layers using high-spatial-resolution particle image velocimetry.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
Vol. 129,
Issue. ,
p.
110469.
Silvestri, S.
and
Pecnik, R.
2021.
Turbulence modulation in thermally expanding and contracting flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 926,
Issue. ,
Bross, Matthew
Scharnowski, Sven
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2021.
Large-scale coherent structures in compressible turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 911,
Issue. ,
Knopp, Tobias
Reuther, N.
Novara, M.
Schanz, D.
Schülein, E.
Schröder, A.
and
Kähler, C.J.
2021.
Experimental analysis of the log law at adverse pressure gradient.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 918,
Issue. ,
Ivashchenko, V A
Zaripov, D I
and
Mullyadzhanov, R I
2021.
The effect of Reynolds number on near-wall reverse flow in a turbulent duct flow.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 2119,
Issue. 1,
p.
012032.
Beresh, Steven J
2021.
Time-resolved particle image velocimetry.
Measurement Science and Technology,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 10,
p.
102003.
Zaripov, Dinar
Ivashchenko, Vladislav
Mullyadzhanov, Rustam
Li, Renfu
Markovich, Dmitriy
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2021.
Reverse flow phenomenon in duct corners at a low Reynolds number.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 8,
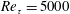 $Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}=5000$. Due to the high spatial and temporal resolution of the measurements, it was possible to resolve and identify uniform-momentum zones in the region
$Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}=5000$. Due to the high spatial and temporal resolution of the measurements, it was possible to resolve and identify uniform-momentum zones in the region 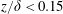 $z/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}<0.15$ or
$z/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}<0.15$ or 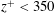 $z^{+}<350$ and to relate them with well known coherent flow motions near the wall. The space–time results confirm that the turbulent superstructures have a strong impact even on the very near-wall flow motion and also their alternating appearance in time and intensity could be quantified over long time sequences. Using the time record of the velocity field, rare localized separation events appearing in the viscous sublayer were also analysed. By means of volumetric particle tracking velocimetry their three-dimensional topology and dynamics could be resolved. Based on the results, a conceptual model was deduced that explains their rare occurrence, topology and dynamics by means of a complex interaction process between low-momentum turbulent superstructures, near-wall low-speed streaks and tilted longitudinal and spanwise vortices located in the near-wall region.
$z^{+}<350$ and to relate them with well known coherent flow motions near the wall. The space–time results confirm that the turbulent superstructures have a strong impact even on the very near-wall flow motion and also their alternating appearance in time and intensity could be quantified over long time sequences. Using the time record of the velocity field, rare localized separation events appearing in the viscous sublayer were also analysed. By means of volumetric particle tracking velocimetry their three-dimensional topology and dynamics could be resolved. Based on the results, a conceptual model was deduced that explains their rare occurrence, topology and dynamics by means of a complex interaction process between low-momentum turbulent superstructures, near-wall low-speed streaks and tilted longitudinal and spanwise vortices located in the near-wall region.




