Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 April 2013
We treat the dielectric decrement induced by excess ion polarization as a source of ion specificity and explore its impact on electrokinetics. We employ a modified Poisson–Nernst–Planck (PNP) model accounting for the dielectric decrement. The dielectric decrement is determined by the excess-ion-polarization parameter  $\alpha $ and when
$\alpha $ and when  $\alpha = 0$ the standard PNP model is recovered. Our model shows that ions saturate at large zeta potentials
$\alpha = 0$ the standard PNP model is recovered. Our model shows that ions saturate at large zeta potentials 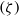 $(\zeta )$. Because of ion saturation, a condensed counterion layer forms adjacent to the charged surface, introducing a new length scale, the thickness of the condensed layer
$(\zeta )$. Because of ion saturation, a condensed counterion layer forms adjacent to the charged surface, introducing a new length scale, the thickness of the condensed layer 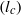 $({l}_{c} )$. For the electro-osmotic mobility, the dielectric decrement weakens the electro-osmotic flow owing to the decrease of the dielectric permittivity. At large
$({l}_{c} )$. For the electro-osmotic mobility, the dielectric decrement weakens the electro-osmotic flow owing to the decrease of the dielectric permittivity. At large 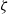 $\zeta $, when
$\zeta $, when 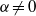 $\alpha \not = 0$, the electro-osmotic mobility is found to be proportional to
$\alpha \not = 0$, the electro-osmotic mobility is found to be proportional to 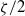 $\zeta / 2$, in contrast to
$\zeta / 2$, in contrast to 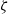 $\zeta $ as predicted by the standard PNP model. This is attributed to ion saturation at large
$\zeta $ as predicted by the standard PNP model. This is attributed to ion saturation at large 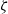 $\zeta $. In terms of the electrophoretic mobility
$\zeta $. In terms of the electrophoretic mobility  ${M}_{e} $, we carry out both an asymptotic analysis in the thin-double-layer limit and solve the full modified PNP model to compute
${M}_{e} $, we carry out both an asymptotic analysis in the thin-double-layer limit and solve the full modified PNP model to compute 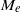 ${M}_{e} $. Our analysis reveals that the impact of the dielectric decrement is intriguing. At small and moderate
${M}_{e} $. Our analysis reveals that the impact of the dielectric decrement is intriguing. At small and moderate 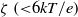 $\zeta ~({\lt }6kT/ e)$, the dielectric decrement decreases
$\zeta ~({\lt }6kT/ e)$, the dielectric decrement decreases 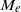 ${M}_{e} $ with increasing
${M}_{e} $ with increasing  $\alpha $. At large
$\alpha $. At large 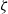 $\zeta $, it is known that the surface conduction becomes significant and plays an important role in determining
$\zeta $, it is known that the surface conduction becomes significant and plays an important role in determining 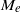 ${M}_{e} $. It is observed that the dielectric decrement effectively reduces the surface conduction. Hence in stark contrast,
${M}_{e} $. It is observed that the dielectric decrement effectively reduces the surface conduction. Hence in stark contrast, 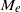 ${M}_{e} $ increases as
${M}_{e} $ increases as  $\alpha $ increases. Our predictions of the contrast dependence of the mobility on
$\alpha $ increases. Our predictions of the contrast dependence of the mobility on  $\alpha $ at different zeta potentials qualitatively agree with experimental results on the dependence of the mobility among ions and provide a possible explanation for such ion specificity. Finally, the comparisons between the thin-double-layer asymptotic analysis and the full simulations of the modified PNP model suggest that at large
$\alpha $ at different zeta potentials qualitatively agree with experimental results on the dependence of the mobility among ions and provide a possible explanation for such ion specificity. Finally, the comparisons between the thin-double-layer asymptotic analysis and the full simulations of the modified PNP model suggest that at large 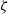 $\zeta $ the validity of the thin-double-layer approximation is determined by
$\zeta $ the validity of the thin-double-layer approximation is determined by  ${l}_{c} $ rather than the traditional Debye length.
${l}_{c} $ rather than the traditional Debye length.