No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Quasi-Sturmian colorings on regular trees
Part of:
Low-dimensional dynamical systems
Graph theory
Discrete mathematics in relation to computer science
Special aspects of infinite or finite groups
Structure and classification of infinite or finite groups
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 August 2019
Abstract
Quasi-Sturmian words, which are infinite words with factor complexity eventually 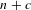 $n+c$ share many properties with Sturmian words. In this article, we study the quasi-Sturmian colorings on regular trees. There are two different types, bounded and unbounded, of quasi-Sturmian colorings. We obtain an induction algorithm similar to Sturmian colorings. We distinguish them by the recurrence function.
$n+c$ share many properties with Sturmian words. In this article, we study the quasi-Sturmian colorings on regular trees. There are two different types, bounded and unbounded, of quasi-Sturmian colorings. We obtain an induction algorithm similar to Sturmian colorings. We distinguish them by the recurrence function.
MSC classification
Primary:
20E08: Groups acting on trees
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2019
References
Aberkane, A.. Words whose complexity satisfies limp (n)/n = 1. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 307(1) (2003), 31–46.Google Scholar
Allouche, J. and Shallit, J.. Automatic Sequences: Theory, Applications, Generalizations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2003.Google Scholar
Cassaigne, J.. Sequences with grouped factors. Developments in Language Theory III (DLT’97). Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, 1998, pp. 211–222.Google Scholar
Coven, E.. Sequences with minimal block growth. II. Math. Syst. Theory 8 (1974/75), 376–382.Google Scholar
Kim, D. H. and Lim, S.. Subword complexity and Sturmian colorings of regular trees. Ergod. Th. & Dynam. Sys. 35(2) (2015), 461–481.Google Scholar
Kim, D. H. and Lim, S.. Continued fraction algorithm for Sturmian colorings of trees. Ergod. Th. & Dynam. Sys. (published online in December 2017).Google Scholar
Lothaire, M.. Algebraic Combinatorics on Words (Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, 90). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002.Google Scholar
Morse, M. and Hedlund, G.. Symbolic dynamics II. Sturmian trajectories. Amer. J. Math. 62(1) (1940), 1–42.Google Scholar
Paul, M.. Minimal symbolic flows having minimal block growth. Math. Syst. Theory 8 (1974/75), 309–315.Google Scholar
Pytheas Fogg, N.. Substitutions in Dynamics, Arithmetics and Combinatorics (Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 1794). Springer, Berlin, 2002.Google Scholar
Rauzy, G.. Suites à termes dans un alphabet fini. Séminaire de théorie des nombres de Bordeaux, Exp. No 25, 1982–1983, 1–16.Google Scholar





