Article contents
Minimal interval exchange transformations with flips
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 April 2017
Abstract
We consider interval exchange transformations of  $n$ intervals with
$n$ intervals with 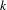 $k$ flips, or
$k$ flips, or 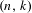 $(n,k)$-IETs for short, for positive integers
$(n,k)$-IETs for short, for positive integers 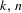 $k,n$ with
$k,n$ with 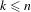 $k\leq n$. Our main result establishes the existence of minimal uniquely ergodic
$k\leq n$. Our main result establishes the existence of minimal uniquely ergodic  $(n,k)$-IETs when
$(n,k)$-IETs when 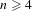 $n\geq 4$; moreover, these IETs are self-induced for
$n\geq 4$; moreover, these IETs are self-induced for 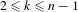 $2\leq k\leq n-1$. This result extends the work on transitivity in Gutierrez et al [Transitive circle exchange transformations with flips. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 26(1) (2010), 251–263]. In order to achieve our objective we make a direct construction; in particular, we use the Rauzy induction to build a periodic Rauzy graph whose associated matrix has a positive power. Then we use a result in the Perron–Frobenius theory [Pullman, A geometric approach to the theory of non-negative matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 4 (1971) 297–312] which allows us to ensure the existence of these minimal self-induced and uniquely ergodic
$2\leq k\leq n-1$. This result extends the work on transitivity in Gutierrez et al [Transitive circle exchange transformations with flips. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 26(1) (2010), 251–263]. In order to achieve our objective we make a direct construction; in particular, we use the Rauzy induction to build a periodic Rauzy graph whose associated matrix has a positive power. Then we use a result in the Perron–Frobenius theory [Pullman, A geometric approach to the theory of non-negative matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 4 (1971) 297–312] which allows us to ensure the existence of these minimal self-induced and uniquely ergodic 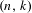 $(n,k)$-IETs,
$(n,k)$-IETs, 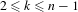 $2\leq k\leq n-1$. We then find other permutations in the same Rauzy class generating minimal uniquely ergodic
$2\leq k\leq n-1$. We then find other permutations in the same Rauzy class generating minimal uniquely ergodic 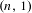 $(n,1)$- and
$(n,1)$- and 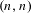 $(n,n)$-IETs.
$(n,n)$-IETs.
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2017
References
- 4
- Cited by




