Article contents
On Erdős–Ko–Rado for Random Hypergraphs II
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 October 2018
Abstract
Denote by 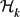 ${\mathcal H}_k$(n, p) the random k-graph in which each k-subset of {1,. . .,n} is present with probability p, independent of other choices. More or less answering a question of Balogh, Bohman and Mubayi, we show: there is a fixed ε > 0 such that if n = 2k + 1 and p > 1 - ε, then w.h.p. (that is, with probability tending to 1 as k → ∞),
${\mathcal H}_k$(n, p) the random k-graph in which each k-subset of {1,. . .,n} is present with probability p, independent of other choices. More or less answering a question of Balogh, Bohman and Mubayi, we show: there is a fixed ε > 0 such that if n = 2k + 1 and p > 1 - ε, then w.h.p. (that is, with probability tending to 1 as k → ∞), 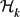 ${\mathcal H}_k$(n, p) has the ‘Erdős–Ko–Rado property’. We also mention a similar random version of Sperner's theorem.
${\mathcal H}_k$(n, p) has the ‘Erdős–Ko–Rado property’. We also mention a similar random version of Sperner's theorem.
MSC classification
- Type
- Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2018
Footnotes
Supported by NSF grant DMS1201337.
References
- 2
- Cited by




