Article contents
Ergodicity of affine processes on the cone of symmetric positive semidefinite matrices
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 September 2020
Abstract
This article investigates the long-time behavior of conservative affine processes on the cone of symmetric positive semidefinite 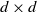 $d\times d$
matrices. In particular, for conservative and subcritical affine processes we show that a finite
$d\times d$
matrices. In particular, for conservative and subcritical affine processes we show that a finite 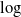 $\log$
-moment of the state-independent jump measure is sufficient for the existence of a unique limit distribution. Moreover, we study the convergence rate of the underlying transition kernel to the limit distribution: first, in a specific metric induced by the Laplace transform, and second, in the Wasserstein distance under a first moment assumption imposed on the state-independent jump measure and an additional condition on the diffusion parameter.
$\log$
-moment of the state-independent jump measure is sufficient for the existence of a unique limit distribution. Moreover, we study the convergence rate of the underlying transition kernel to the limit distribution: first, in a specific metric induced by the Laplace transform, and second, in the Wasserstein distance under a first moment assumption imposed on the state-independent jump measure and an additional condition on the diffusion parameter.
MSC classification
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Applied Probability Trust 2020
References
- 1
- Cited by





