Book contents
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 Infectious Conditions
- Section 2 Inflammatory Conditions
- Section 3 Hereditary and Genetic Conditions and Malformations
- Section 4 Vascular Conditions of the Eyes, Ears, and Brain
- Section 5 Disorders Involving Abnormal Coagulation
- Section 6 Systemic Disorders That Also Involve the Cerebrovascular System
- Chapter 47 Microscopic Polyangiitis and Polyarteritis Nodosa
- Chapter 48 Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
- Chapter 49 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Cerebrovascular Disease
- Chapter 50 Rheumatologic Diseases and Strokes
- Chapter 51 Hyperviscosity and Strokes
- Chapter 52 Calcium, Hypercalcemia, Magnesium, and Brain Ischemia
- Chapter 53 Strokes and Substance Abuse
- Chapter 54 Cancer and Paraneoplastic Strokes
- Chapter 55 Malignant Atrophic Papulosis
- Chapter 56 Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Strokes
- Chapter 57 Sweet Syndrome
- Chapter 58 Strokes Associated with Nephrotic Syndrome and Other Renal Diseases
- Chapter 59 Epidermal Nevus Syndrome
- Chapter 60 Sneddon Syndrome
- Chapter 61 Bone Disorders and Cerebrovascular Diseases
- Chapter 62 Scleroderma
- Chapter 63 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- Chapter 64 Radiation-Induced Vascular Disease
- Chapter 65 Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- Section 7 Non-Inflammatory Disorders of the Arterial Wall
- Section 8 Venous Occlusive Conditions
- Section 9 Vasospastic Conditions and Other Miscellaneous Vasculopathies
- Index
- Plate Section (PDF Only)
- References
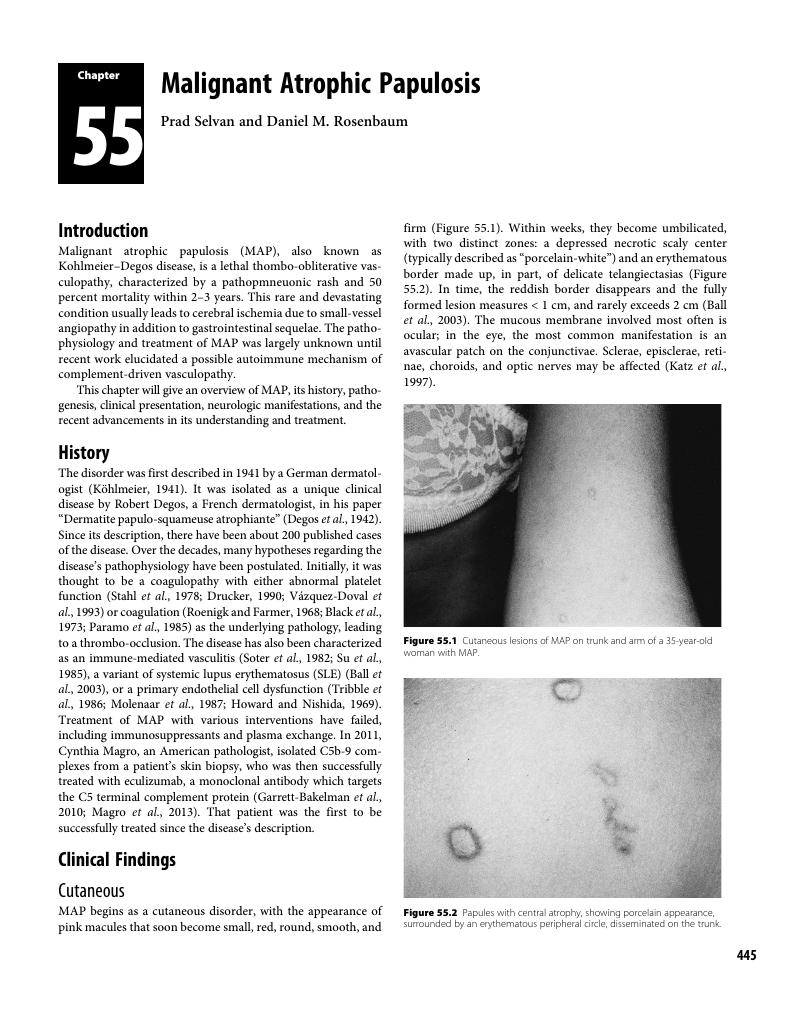
Chapter 55 - Malignant Atrophic Papulosis
from Section 6 - Systemic Disorders That Also Involve the Cerebrovascular System
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 June 2018
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 Infectious Conditions
- Section 2 Inflammatory Conditions
- Section 3 Hereditary and Genetic Conditions and Malformations
- Section 4 Vascular Conditions of the Eyes, Ears, and Brain
- Section 5 Disorders Involving Abnormal Coagulation
- Section 6 Systemic Disorders That Also Involve the Cerebrovascular System
- Chapter 47 Microscopic Polyangiitis and Polyarteritis Nodosa
- Chapter 48 Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
- Chapter 49 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Cerebrovascular Disease
- Chapter 50 Rheumatologic Diseases and Strokes
- Chapter 51 Hyperviscosity and Strokes
- Chapter 52 Calcium, Hypercalcemia, Magnesium, and Brain Ischemia
- Chapter 53 Strokes and Substance Abuse
- Chapter 54 Cancer and Paraneoplastic Strokes
- Chapter 55 Malignant Atrophic Papulosis
- Chapter 56 Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Strokes
- Chapter 57 Sweet Syndrome
- Chapter 58 Strokes Associated with Nephrotic Syndrome and Other Renal Diseases
- Chapter 59 Epidermal Nevus Syndrome
- Chapter 60 Sneddon Syndrome
- Chapter 61 Bone Disorders and Cerebrovascular Diseases
- Chapter 62 Scleroderma
- Chapter 63 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- Chapter 64 Radiation-Induced Vascular Disease
- Chapter 65 Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- Section 7 Non-Inflammatory Disorders of the Arterial Wall
- Section 8 Venous Occlusive Conditions
- Section 9 Vasospastic Conditions and Other Miscellaneous Vasculopathies
- Index
- Plate Section (PDF Only)
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Uncommon Causes of Stroke , pp. 445 - 447Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2018



