Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Foreword by Alan Daneman
- Foreword by Phyllis A. Dennery
- Foreword by Avroy A. Fanaroff
- Preface
- 1 Introduction to principles of the radiological investigation of the neonate
- 2 Evidence-based use of diagnostic imaging: reliability and validity
- 3 The chest, page 11 to 40
- The chest, page 41 to 69
- 4 Neonatal congenital heart disease
- 5 Special considerations for neonatal ECMO
- 6 The central nervous system
- 7 The gastrointestinal tract
- 8 The kidney
- 9 Some principles of in utero and post-natal formation of the skeleton
- 10 Metabolic diseases
- 11 Catheters and tubes
- 12 Routine prenatal screening during pregnancy
- 13 Antenatal diagnosis of selected defects
- Index
- References
The chest, page 41 to 69
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 March 2012
- Frontmatter
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Foreword by Alan Daneman
- Foreword by Phyllis A. Dennery
- Foreword by Avroy A. Fanaroff
- Preface
- 1 Introduction to principles of the radiological investigation of the neonate
- 2 Evidence-based use of diagnostic imaging: reliability and validity
- 3 The chest, page 11 to 40
- The chest, page 41 to 69
- 4 Neonatal congenital heart disease
- 5 Special considerations for neonatal ECMO
- 6 The central nervous system
- 7 The gastrointestinal tract
- 8 The kidney
- 9 Some principles of in utero and post-natal formation of the skeleton
- 10 Metabolic diseases
- 11 Catheters and tubes
- 12 Routine prenatal screening during pregnancy
- 13 Antenatal diagnosis of selected defects
- Index
- References
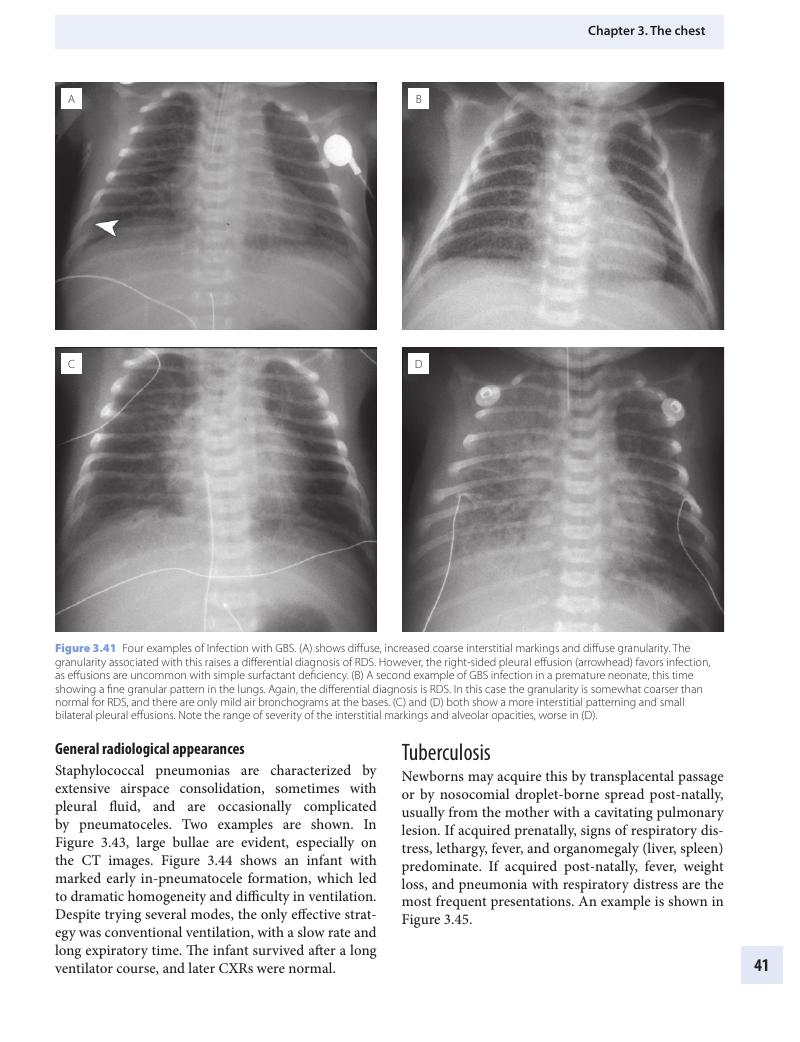
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Imaging of the Newborn , pp. 41 - 69Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2011